
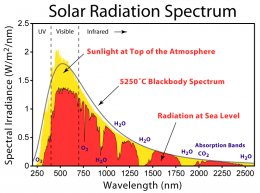
 In space, the sun transfers heat via radiation to equipment and astronauts. Although the sun’s peak emission is in the visible region (about 500 nm), you can see that there is also a fair amount IR (infrared) and UV (ultraviolet) emitted as well at the top of the atmosphere.
In space, the sun transfers heat via radiation to equipment and astronauts. Although the sun’s peak emission is in the visible region (about 500 nm), you can see that there is also a fair amount IR (infrared) and UV (ultraviolet) emitted as well at the top of the atmosphere.
To control the surface temperature of an object that is exposed to IR (heat waves), NASA wraps its equipment with a metallic reflector that reflects IR to keep it from getting “hot.” The common reflectors are aluminum, silver, copper and gold. Below, the plot of reflectance vs. wavelength shows that all four metals are good IR-reflectors since the reflectance is close to 100% for wavelengths greater than 700 nm (λ ≥ 700 nm).
So why use gold? It’s most likely the same reason why they use gold extensively in circuit boards. (i) Gold does not corrode or rust while silver and copper does, which would reduce reflectance (by the way this happens before takeoff) and (ii) it’s a lot easier to work with gold than aluminum.
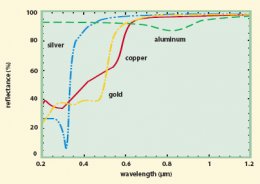 The outer sun visor is made from a polycarbonate plastic and coated with a thin layer of gold. This combination gives complete protection to the astronaut. Why? Your eyes can focus both visible and near IR light onto your retina equally well. Your eye has visible receptors but not IR ones. When intense visible light hits these receptors, the receptors transmit information letting you know that this is painful and will cause damage if you don’t either close them or look away. On the other hand, without IR receptors, you wouldn’t realize that your eye was being “burned” with an intense IR source. Therefore, astronauts need IR protection from intense sunlight above the earth atmosphere. From the plot above, using a gold-coated visor reflects almost all IR but gold will also transmit about 60% of visible as well as UV light for about λ ≤ 500 nm. According to the plot above, with the visor down you would see a blue-green hue to objects). On the other hand, about 60% of UV is transmitted through the gold but a polycarbonate plastic visor has excellent visible transmittance but absorbs/reflects almost all UV as shown below.
The outer sun visor is made from a polycarbonate plastic and coated with a thin layer of gold. This combination gives complete protection to the astronaut. Why? Your eyes can focus both visible and near IR light onto your retina equally well. Your eye has visible receptors but not IR ones. When intense visible light hits these receptors, the receptors transmit information letting you know that this is painful and will cause damage if you don’t either close them or look away. On the other hand, without IR receptors, you wouldn’t realize that your eye was being “burned” with an intense IR source. Therefore, astronauts need IR protection from intense sunlight above the earth atmosphere. From the plot above, using a gold-coated visor reflects almost all IR but gold will also transmit about 60% of visible as well as UV light for about λ ≤ 500 nm. According to the plot above, with the visor down you would see a blue-green hue to objects). On the other hand, about 60% of UV is transmitted through the gold but a polycarbonate plastic visor has excellent visible transmittance but absorbs/reflects almost all UV as shown below.
RELATED VIDEO











